In the dynamic world of healthcare, advancing clinical capabilities is essential for delivering precise, high-quality, patient-centered care. Accurate and reliable laboratory testing is crucial for the success of both clinical and preclinical research. However, ensuring consistency in lab results can be challenging due to variations in testing facilities, personnel, equipment, and even environmental factors like temperature and humidity. This is where central laboratory services come in. They provide standardized testing that guarantees consistency and reliability across different sites in multi-site studies. This standardization is essential for both clinical and preclinical research, as it enhances the accuracy and dependability of study results, leading to more robust and reproducible scientific discoveries.
Central laboratory services play a vital role in supporting complex, multi-site clinical trials. Contract research organizations (CROs) that offer these services handle project management, prepare necessary kits, and provide logistical support. They perform laboratory tests and analyses needed for sample testing, compile and report test results, and manage electronic data and document archiving. Additionally, they oversee the collection, receipt, management, storage, and disposal of samples, ensuring smooth and efficient trial operations.
The Need for and Benefits of Central Laboratory Services
The need for central laboratory services is emphasized by their ability to ensure standardization and consistency across multiple study sites, with consistent sample handling, testing protocols, and data reporting essential for reliable results. Rigorous quality control measures minimize errors and enhance data integrity, meeting the high standards demanded by regulatory agencies for drug approvals. Efficient sample management streamlines collection, transportation, and storage, ensuring timely analysis crucial for trial success. For multinational clinical trials, central labs harmonize services across regions, bridging geographical gaps and facilitating seamless data exchange.
The benefits of central laboratory services include cost savings by reducing infrastructure expenses for pharmaceutical companies and leveraging economies of scale for CROs. Central labs employ specialized scientists and cutting-edge equipment, accessing advanced technologies that improve assay accuracy. They also mitigate risks associated with decentralized testing, providing consistent results that enhance trial validity. Additionally, centralized data management allows real-time tracking and analysis, giving sponsors and CROs valuable insights for decision-making.
The Role of Central Labs in Clinical Trials:

Central labs act as specialized scientific hubs, processing samples and centralizing data for efficient analysis while collaborating with trial investigators and sponsors to align study objectives with standard operating procedures. Throughout the trial lifecycle, they manage sample collection, engage with study sites to address issues, and ensure reliable analysis through rigorous quality control.
Central Labs vs. Local Labs: Unravelling the Distinction
A central laboratory is an advanced facility where samples from a trial’s investigator sites are centrally processed and tested using standardized procedures and equipment. In contrast, a local laboratory performs limited testing for one or a few study sites within a multi-site study. While local labs may offer faster processing times, they generally lack the extensive range of specialty testing services (such as flow cytometry and genomics) and the high-quality, combinable data that central labs provide.
Clinical trials are crucial for bringing drugs to market but carry a high investment risk, with less than 12% of drugs reaching commercialization. Patient recruitment is a major cost driver in clinical trials, but decentralization offers a way to reduce financial burdens. Studies indicate significant financial benefits for sponsors, including returns of up to 5 and 13 times the investment for phase 2 and 3 studies, respectively. Centralized trials often impose physical and emotional burdens on patients and may result in biased outcomes due to underrepresentation of certain populations.
This issue is especially pronounced in Phase I studies, where intensive clinical visits can lead to dropout rates as high as 40%. Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs), conducted at local points of care or in patients’ homes, address these challenges by using remote monitoring and data collection, reducing patient burden and enhancing study efficiency. Since 2020, there has been a 50% increase in DCTs, highlighting their potential to transform the drug development process.
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) with a focus on significant shifts
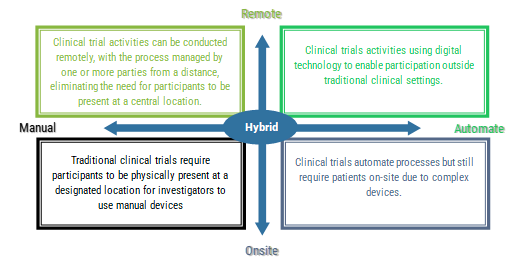
The shift from traditional central laboratory services to decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) represents a significant transformation in clinical research.
Hybrid models offer a balanced approach, maintaining the high standards of central laboratory services while incorporating the flexibility and patient-centric benefits of DCTs. This approach not only improves the efficiency and inclusivity of clinical trials but also enhances data integrity and regulatory compliance. As the landscape of clinical research continues to evolve, hybrid models represent the future of clinical trials, integrating advanced technologies and patient-centered practices to optimize drug development and deliver better health outcomes. Telemedicine use in clinical trials is set to continue gaining momentum along with continued rise of institutions and non-profit organisations utilising decentralisation. The pandemic accelerated the adoption of DCTs, by small and medium-sized CROs.
Hybrid Models are evolving from uncertainty to a more established and strategic approach, benefiting both patients and trial sponsors. Europe has been significantly impacted by local-specific translation of European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommendations related to DCT implementation. In the US, oncology studies have gained momentum in this space, with concierge services providing tech support and assisting patients with direct-to-patient material shipments.
Sanofi has embraced hybrid and decentralized clinical trials, leveraging digital devices and patient-centric tools, with its development programs now entirely informed by patients and significantly enhanced by technology.
With the increased adoption of decentralized and hybrid models, regulatory guidance is evolving to ensure the safety and data quality of on-site trials. Sponsors integrating DCT elements must thoroughly understand Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This includes knowing what personal data study teams collect, how it is processed, and what records must be maintained for regulatory compliance. As drug development increasingly relies on remote monitoring and digital patient practices, the importance of sponsors partnering with CROs that comprehend data privacy and compliance intricacies. These partners can help develop a comprehensive data collection and management strategy that adheres to all necessary regulations.
Oncology clinical trials often require demanding on-study visits, such as imaging and biopsies, creating significant barriers for patients, especially those living far from major medical centers. Geographic disparities further hinder accessibility, as seen in the United States, Europe and China. Many in-person visits do not produce clinically significant data, prompting a need for better trial designs. The digital transformation accelerated the adoption of remote and hybrid trials, utilizing telemedicine, local labs, and home-based monitoring technologies.
Way Forward
Examples include the international CodeBreaK100 trial and ongoing studies like ON TRAX, which employ remote data collection to improve trial efficiency and patient outcomes. To make trials truly patient-centric, patients should be active partners in trial design and implementation. Efforts should focus on reducing patient burden without compromising safety or data quality, incorporating telemedicine, wearable devices, and remote drug shipments. Ensuring diverse and inclusive participation, especially from racial minorities and rural areas, is essential. Multi-regional trials and AI-driven remote monitoring can further enhance accessibility and applicability of study results, with the alliance advocating for protocol amendments to deliver care conveniently for patients.





