Key takeaways
- Effective Procurement Management: Successful procurement involves a comprehensive process, including supplier research, onboarding, contract management, and maintaining strong supplier relationships to ensure smooth operations and efficient workflows within the supply chain.
- Budget and Cost Control: Adhering to the procurement budget is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, which includes price negotiation and monitoring procurement spend to optimize costs and align with financial plans.
- Diverse Procurement Needs: The procurement cycle covers various aspects such as direct procurement, indirect procurement, goods procurement, and services procurement, all of which are essential for meeting the company’s diverse needs.
- Modern E-Procurement Practices: Leveraging e-procurement and supplier exchange technologies enhances communication and transaction management, streamlining the procurement process and fostering better supplier relationships.
What is procurement and purchasing?
Purchasing and procurement both relate to the sourcing and purchase of products and services. Procurement, in its simplest form, involves buying things, but if you ask any business person the same question, the answer may not be that simple. Most business people will say that any procurement process involves a series of activities that are crucial for an organization to procure the best products or services at the best price. Since most organizations today end up spending a lot of their revenue on purchasing goods, effective management of the entire procurement process becomes vital for companies looking to sustain themselves in today’s economy. Procurement is, for many companies, the major reason behind their success and will continue to gain importance among businesses of all sizes in the years to come.
Since both purchasing and procurement deal with the acquisition of goods, most of us have started using the terms purchasing and procurement interchangeably. But despite their numerous similarities, they do have very different meanings. Procurement, as discussed previously, is a multi-faceted process and involves steps such as supplier selection, screening, negotiating payment terms, setting up contracts, and finally purchasing the desired goods at the best possible rates. Purchasing, on the other hand, is a smaller process within the overarching procurement process. It basically refers to the process of how products or services are ordered and can be described as the transactional facet of the overall procurement process. Now that you know the basic differences between purchasing and procurement, let’s walk you through some of the major differences between the purchasing and procurement process.
The Procurement Process

In any business scenario, procurement is deeply intertwined with several core business functions. It is therefore influenced by the businesses’ corporate strategy and its commitment towards aligning both functions. To establish an effective procurement process, follow the four steps given below:
Step 1: Establish your company’s identity and know more about your values and ideals
Establishing your company’s identity and values in procurement is vital. Define your core identity, values, and a code of ethics to guide your purchasing processes. Ensure all employees understand and embrace these principles through training and communication. Assess suppliers for alignment with your values, considering ethical practices and sustainability. Encourage suppliers to adopt similar codes of conduct. Prioritize transparency and reporting, regularly reviewing and improving your approach. Implement audits, and accountability measures, and engage with stakeholders to maintain alignment with your company’s values and ideals in the procurement process, ensuring responsible and ethical practices
Step 2: Think about market placement and whether you want to appeal to a large or specific client base
In the procurement process, it’s vital to consider your market placement strategy. Determine whether you intend to cater to a broad or specific client base. Aiming for a broad client base focuses on mass appeal and high sales volumes, while a niche approach tailors offerings to a specialized, smaller group. Each has its benefits, including economies of scale for the broad market and higher margins for the niche. Your choice should align with your business objectives, resources, and the nature of your procurement needs, shaping your procurement strategies accordingly.
Step 3: Assess your company’s capabilities and find out your major strengths and weaknesses
Assessing your company’s capabilities is a critical step in the procurement process. Identify your core strengths, which may include negotiation skills, supplier relationships, or advanced technology. Concurrently, acknowledge weaknesses like limited resources, lack of supplier diversity, or inefficient processes. Understanding these internal aspects helps in strategic planning, risk mitigation, and optimization of procurement practices. It also allows you to leverage strengths and address weaknesses to enhance efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and competitiveness in your procurement efforts.
Step 4: Iron out management issues before they start affecting the company’s productivity
Addressing management issues proactively is essential in the procurement process to prevent disruptions in productivity. By identifying and resolving potential challenges in leadership, communication, and decision-making early on, you ensure smoother operations. These issues could include unclear roles, lack of accountability, or inadequate communication between departments. By ironing out these problems, you promote efficiency, reduce delays, and maintain a seamless procurement process, ultimately benefiting the company’s productivity, cost-effectiveness, and overall success.
A key thing to note here is that the steps mentioned above are not separated from each other but are often closely entwined.
How Procurement Works
Procurement can require a substantial portion of a company’s resources to manage. The procurement process encompasses a series of steps starting from the initial purchase request to price negotiation and final purchase. This process is typically dictated by company standards centralized by controls from accounts payable, ensuring that every step adheres to established protocols. The procurement cycle involves several key stages, including supplier research, supplier onboarding, contract management, and the actual purchasing of goods and services. Effective workflow management within the supply chain is crucial to maintain smooth operations and ensure timely delivery of materials.
Developing strong relationships with each supplier is vital for successful direct procurement. These relationships can lead to better terms during price negotiation and ensure a reliable source of quality materials. A procurement budget provides managers with a specific value they can spend, guiding them on how to allocate resources efficiently. This system is a key part of a company’s strategy because the ability to purchase specific materials and services can determine if operations are even profitable.
Managing procurement effectively involves a comprehensive understanding of the procurement process and careful oversight of the procurement cycle. This includes everything from the initial purchase request to supplier onboarding and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, all within the constraints of the procurement budget.
The Purchasing Process
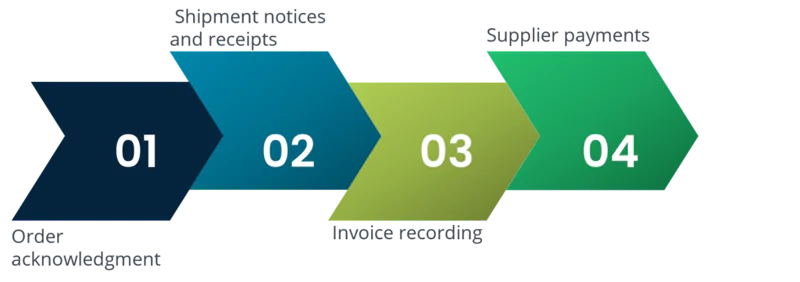
When you think of purchasing and procurement, always remember that purchasing is a smaller part of the overarching procurement process. Since it involves the buying of actual products or services, it includes the transactional part too, which is receiving goods and the subsequent payment. In the overall procurement process, purchasing is only related to:
Step 1: Order acknowledgement
Acknowledging an order is an essential step in the purchasing process. It involves the formal acceptance of a purchase order by the supplier or vendor. The process starts with the buyer (the organization) issuing a purchase order (PO) to a supplier, which outlines the products or services to be acquired, the quantities, prices, delivery terms, and other relevant terms and conditions. Once the supplier receives the PO, they review it carefully before sending an order confirmation or acknowledgment to the buyer. This document serves as a formal acceptance of the PO and confirms the agreement to supply the requested products or services. It should match the terms and conditions outlined in the original PO.
Step 2: Shipment notices and receipts
Shipment notices and receipts are integral steps in the purchasing process. Shipment notices, often generated by suppliers, provide advanced notification to buyers about the impending delivery, including tracking details and expected arrival times. Upon receipt of the shipment, buyers generate receipts to confirm the delivery’s accuracy and condition. These documents serve as proof of successful delivery and are crucial for inventory management and payment processing. They help ensure that the ordered goods match expectations and are in good condition, preventing discrepancies and facilitating the efficient flow of products through the supply chain.
Step 3: Invoice recording
Invoice recording is a pivotal step in the purchasing process. After receiving goods or services, the buyer’s accounting department records the supplier’s invoice, verifying that the charges align with the purchase order and agreed-upon terms. This step also includes data entry into financial systems and validation of payment details. Accurate and timely invoice recording is essential for cost control, tracking expenses, and ensuring timely payments, ultimately maintaining positive supplier relationships and financial transparency within the procurement process.
Step 4: Supplier payments
Supplier payments are a critical component of the purchasing process. Once invoices are verified and recorded, the finance department processes payments to suppliers. Payments can be made via various methods, such as checks, electronic funds transfers, or credit cards, depending on the agreed-upon terms. Timely and accurate payments are essential to maintain strong supplier relationships, ensure a smooth supply chain, and uphold the company’s creditworthiness. Managing cash flow and adhering to negotiated payment terms are integral to successful supplier payments in the procurement process.
The steps discussed here shouldn’t be tailored to suit the scope of your business since the nature and size of your business do not influence them.
How Purchasing Works
Purchasing is a vital function within a company’s procurement cycle that involves several key steps to ensure the acquisition of goods and services meets the organization’s needs efficiently and cost-effectively. The process typically begins with a purchase request and involves thorough supplier research to identify potential suppliers. Once suitable suppliers are identified, the next step is supplier onboarding, which includes the vetting process to ensure they meet the company’s standards and requirements. Establishing strong supplier relationships is crucial for smooth operations and future negotiations.
The procurement budget plays a significant role in guiding purchasing decisions, ensuring that the company’s expenditures align with financial plans. This budget dictates how much can be spent on goods procurement, services procurement, direct procurement, and indirect procurement. After supplier onboarding, contract management becomes essential to oversee agreements and ensure compliance with terms and conditions. A critical aspect of purchasing is price negotiation, where the goal is to obtain the best possible terms and pricing from suppliers. With contracts in place, the purchasing department can issue a purchase order to formalize the transaction. The procurement spend must be monitored carefully to stay within budget and optimize costs.
Modern purchasing practices often involve e-procurement, which leverages digital platforms for more efficient processing and supplier exchange, enabling better communication and transaction management with suppliers. Effective purchasing relies on these interconnected steps to ensure that the company’s procurement needs are met efficiently and within budget, fostering strong supplier partnerships and maintaining smooth operational workflows.
Want more information of the major differences between the purchasing and procurement process?
Conclusion
Effective purchasing and procurement are critical for the smooth operation of any business, ensuring that the workflow within the supply chain is uninterrupted and efficient. The procurement process begins with a purchase request and involves comprehensive supplier research, supplier onboarding, and contract management to establish and maintain strong relationships with suppliers. Adhering to the procurement budget, companies engage in price negotiation to secure the best terms and pricing. The procurement cycle encompasses direct procurement, indirect procurement, goods procurement, and services procurement, all of which contribute to the overall success of the company’s procurement strategy. The issuance of purchase orders formalizes transactions, and ongoing monitoring of procurement spend ensures alignment with financial goals. Modern practices like e-procurement streamline the process, facilitating better communication and transaction management through supplier exchange. Ultimately, a well-managed procurement function strengthens supplier relationships and enhances the organization’s ability to meet its procurement needs effectively and cost-efficiently.




