Key takeaways
- Understanding the public procurement process is crucial for companies aiming to compete for lucrative projects and secure work opportunities.
- The public procurement process involves several key steps, including requirement identification, scoping, determining procurement methods, exploring sourcing options, evaluating submissions, and managing contracts.
- Challenges in public and private sector procurement include lack of transparency, communication gaps, and cost management concerns, which can be addressed through improved processes and technology adoption.
- Procurement practices in both sectors have significant social, environmental, and economic impacts, including promoting social causes, supporting sustainability, and contributing to job creation.
- Enhancing transparency, communication, and cost-management strategies can lead to more effective procurement operations and positive societal outcomes in both public and private sectors.
In today’s changing economic environment, public works provide the corporate sector with immense opportunities to compete for profitable work. Therefore, understanding the public procurement process is critical to compete for such projects and being eligible for work.
All levels of government, including Federal, state, and local agencies select potential vendors through competition. Public organizations advertise, collect information, and accept offers to secure the necessary goods and services. The process includes Invitations for Bids, Requests for Proposals, Requests for Qualifications, Requests for Letters of Interest, and Invitations to Negotiate. The responses are then evaluated based on the needs of the organization without price being the determinative factor. However, many organizations still face certain challenges when it comes to improving the public procurement process. Here are the key steps involved in the public procurement process.
Want to know how you can improve the public procurement process flow?
Steps Involved in the Public Procurement Process
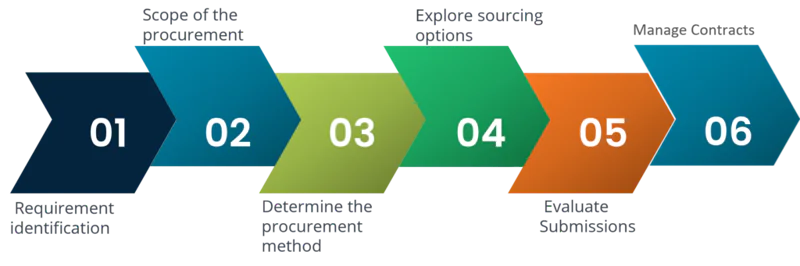
Step 1: Requirement identification
When it comes to procurement, organizations must first determine their objectives and establish a clear scope of requirements. To do this, they should conduct thorough market research to gain insights and understand the capabilities and limitations. While doing so, organizations must also ensure probity arrangements and comply with government transparency requirements. To clearly describe their requirements, organizations create detailed specifications that include technical requirements, performance criteria, quality standards, quantities, and other relevant details. These specifications must be clear, concise, and unambiguous to prevent misunderstandings.
Step 2: Scope of the procurement
Organizations heavily rely on the procurement of rights products to carry out their operations. To ensure that the highest standards are met, some organizations have established protocols to help determine product specifications. The selection of goods or services to be purchased is subject to coordinated procurement arrangements that must be strictly adhered to. Once the products or services have been selected, the next step is to estimate the value of procurement and comply with the rules set by the government entity. This step ensures that all relevant aspects, such as technical specifications, delivery schedules, budget constraints, and regulatory compliance, are considered. The procurement scope serves as the foundation for subsequent steps, including supplier selection, bidding, and contract management.
Step 3: Determine the procurement method
In a public procurement process, it depends on the organization whether they want open tenders or limited tenders. Open tenders generally involve one stage (Request for Tender) and need to be advertised on the official website. Limited tenders are directly asked from or more suppliers. In this, the organization qualifies suppliers to determine the best products.
Step 4: Explore sourcing options
Notify the market to obtain products. For open tenders, ensure that the minimum requirements are met. Include essential information in the request documentation to enable suppliers to develop and lodge competitive and compliant submissions. Also, use appropriate limitation of liability and standard contract clauses to improve the public procurement process.
The inability to improve the public procurement process can restrict companies from procuring the best products for their businesses. Stay a step ahead by contacting our procurement platform to gain exclusive insights to improve the public procurement process cycle.
Step 5: Evaluate Submissions
To improve the public procurement process, it is important to handle any unintentional errors in tenders according to the established guidelines. Additionally, conducting a financial viability assessment of preferred suppliers can be beneficial. To ensure an informed decision, it is essential to provide the delegate with adequate documentation and information.
Step 6: Manage Contracts
Developing a contract management plan is crucial for organizations to help understand and implement obligations under the contract. Organizations should assess contract extension options based on value-for-money and in accordance with the contract terms.
Challenges in Public and Private Sector Procurement
While there are many differences between public and private sector procurement, there are also some common challenges that organizations in both sectors face.
One of the biggest challenges is the lack of transparency in the procurement process. In the public sector, this is exacerbated by the complex legal requirements that organizations have to comply with. In the private sector, the lack of transparency is often due to the lack of technology adoption.
Another challenge is the lack of communication between stakeholders in the procurement process. The complexity of legal requirements makes it difficult for public sector organizations to communicate effectively. In the private sector, the lack of communication is again due to the lack of technology adoption, which can lead to siloed processes.
Finally, there is the challenge of cost management. In the public sector, cost management is a major concern, as organizations are bound by strict budget limits.
To address these challenges, organizations must focus on improving transparency, enhancing communication, and implementing efficient cost-management strategies in their procurement operations. This may involve adopting e-procurement systems to streamline processes, ensuring compliance with public procurement laws and legal requirements, and leveraging negotiation skills to optimize supplier contracts. Ultimately, effective procurement practices can have a significant social impact and contribute to the overall success of organizations in both the public and private sectors.
Social Impact: Public and Private Sector Procurement
Procurement serves as a vital function in both public and private sectors, wielding considerable influence over societal dynamics. In public realms, it frequently serves as a means to champion social causes, facilitating access to vital services and fostering economic empowerment among marginalized segments. Conversely, in the private sector, procurement typically targets operational efficiency and cost reduction.
Beyond societal impacts, procurement practices in both sectors wield considerable environmental implications. With a growing emphasis on sustainability, organizations are increasingly adopting eco-friendly procurement strategies, which entail sourcing from recycled materials and supporting local suppliers. Moreover, efforts are underway to minimize environmental footprints by embracing sustainable materials and curbing waste generation.
Furthermore, procurement activities significantly contribute to job creation dynamics. In public sectors, procurement initiatives often serve as engines for job creation, particularly in underprivileged areas. Similarly, in the private sector, procurement strategies are tailored to bolster local economies and spur employment opportunities.

Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of procurement, whether in the public or private sector, demands meticulous attention to various facets. E-procurement systems offer a pathway to streamlining processes, ensuring compliance with legal requirements, and enhancing transparency. Effective procurement operations hinge on adeptly negotiating terms, implementing contracts, and managing suppliers across all phases of the procurement process. Procurement managers play a pivotal role in orchestrating these efforts, supported by procurement teams equipped with robust procurement software. By prioritizing cost management and embracing sustainable practices, organizations can amplify their social impact, fostering economic empowerment and job creation while mitigating environmental footprints. In essence, effective procurement practices are instrumental in driving organizational success and societal progress alike.




