Key takeaways
- Starch Market Dynamics: The starch market is influenced by diverse factors, including food manufacturers’ demands for quality ingredients, modified starch suppliers’ offerings, and consumer preferences for safe and affordable products, with corn starch being a predominant choice.
- Supplier Performance Evaluation: Buyers in the starch market can assess supplier performance based on criteria such as service resolution rate, inventory management effectiveness, plant utilization rate, turnaround time, and logistics capabilities to ensure reliable partnerships.
- Optimized Starch Preparation: From starch source selection to quality control and storage, a systematic procedure ensures the production of high-quality starch tailored to various applications, including food processing and industrial uses.
- Modified Starch Supplier Selection: Choosing the right modified starch supplier involves evaluating aspects like product quality, cost, industry experience, safety protocols, and delivery services to secure a reliable source of high-quality modified starch products for food processing applications.
List of best starch manufacturers in the world
- DM.
- Cargill.
- Ingredion (Penford Products)
- Tate & Lyle Americas.
- Roquette.
- Argo.
- Gea
If you ever wondered why your rice is clumped together or potato sticks to the pan, it is because of starch, a common carbohydrate found in staple starchy foods such as rice, potatoes, wheat, maize, and cassava. For plants, starch is an efficient way of storing more energy in less space. In industrial applications, starch has a wide variety of uses ranging from use to stiffen the textiles, give strength and shape to paper, add taste to beverages and confectionary items, to its use in various consumer products. Starch manufacturers produce different kinds of starch such as maize starch, potato starch, and wheat starch, but cornstarch is the most common form. The procurement market intelligence report from SpendEdge states that corn starch accounted for nearly 57% of the global starch production capacity by raw material during 2016.
Starch market: An overview
The starch manufacturer market is a vibrant landscape shaped by various factors such as food manufacturers’ demand for quality ingredients, modified starch suppliers’ offerings, and consumer preferences for safe and affordable products. Within this market, corn starch stands out as a staple ingredient, meeting the diverse needs of food manufacturers and consumers alike.
In this competitive arena, suppliers vie for attention by emphasizing product quality, affordability, and adherence to safety protocols. Industry experience plays a crucial role, as seasoned manufacturers leverage their knowledge to ensure the highest standards of quality and safety in their products.
Key considerations for stakeholders include the reputation of suppliers, encompassing their commitment to quality and safety, as well as the efficiency of their delivery services. Testing procedures are paramount, aligning with industry standards to guarantee the integrity of starch products.
Moreover, the market’s diversity extends to the product range, with offerings ranging from high-quality, affordable corn starch to specialized variants like tapioca and potato starch. Exceptional starch manufacturers distinguish themselves through their manufacturing units and robust supply chains, ensuring consistent delivery of top-notch products to food manufacturers worldwide.
With multiple starch manufacturers and suppliers located across the world, it is essential to evaluate supplier performance and competencies to make decisions for future contracts. So how can buyers assess supplier performance in the global starch market?
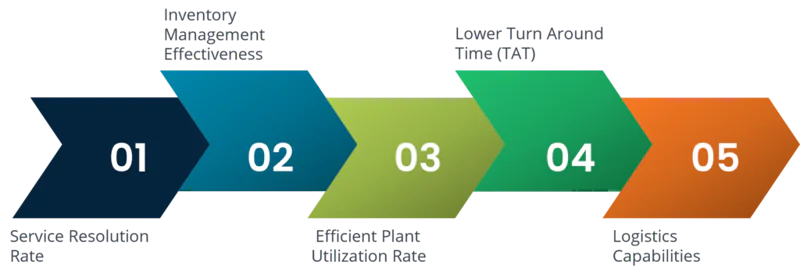
Supplier Evaluation Criteria in Starch Market
#1- Service Resolution Rate
Suppliers ability to respond to buyer’s complaints in terms of quality of the starch, logistics issues, quantity, and packaging issues is a crucial indicator of the supplier performance. Ideally, buyers raise such complaints through complaint registration portal or email to which supplier should respond and ensure resolution within six weeks from the date the complaint was registered.
#2- Inventory Management Effectiveness
Buyers prefer to engage with suppliers who are reliable in terms of ability to provide effective inventory management. To assess supplier’s effectiveness in inventory management, the buyer can use metrics such as reduction in average lead time, which should be within a week for local suppliers, 15-20 days for regional suppliers, and within a month for global sourcing of starch. Additionally, buyers should also ensure that starch manufacturers have adequate safety stock inventory in case of unusual demands. Other things to look for is JIT adherence and use of automated inventory management systems.
#3- Efficient Plant Utilization Rate
Buyers can evaluate starch manufacturers based on their plant utilization rate; a higher percentage is indicative of lower variable costs. It signifies that the buyers can source starch from the suppliers at a lower rate. An ideal plant utilization rate in the starch industry is about 50%-60% of the total capacity.
#4- Lower Turn Around Time (TAT)
Apart from ensuring on-time delivery, starch suppliers should have a quick turnaround time (TAT) to respond to fluctuations in buyer’s demand without any degradation in starch quality. Buyers will ideally stick around with starch manufacturers that can fulfill buyers needs in terms of JIT delivery of starch. In the starch market, an ideal turnaround time is considered to be around 4-5 days from the date of requirement.
#5- Logistics Capabilities
The transportation of starch is not straightforward as it looks. Complications arise due to the difference in transportation laws across borders and complexity in packaging due to exposure to heat or moisture. To evaluate supplier’s logistics capabilities, buyers can assess the ratio of shipments damaged by shipments delivered.
Read more about the supplier assessment criteria for starch manufacturers along with pricing insights, sourcing strategy, key starch suppliers, procurement best practices and cost modeling in SpendEdge’s upcoming report on the global starch market.
Optimized procedure for starch preparation
Starch Source Selection:
The starting step is the selection of an appropriate source of starch based on your intended application, common sources include corn, potato, rice, and wheat. Different sources have varying properties, so the one that aligns with your desired outcome is chosen.
Raw material preparation:
This step of the chronological process involves cleaning the raw material to get rid of contaminants, waste, and filth, and the raw material should be ground or milled to remove the cell walls and liberate the starch granules.
Extraction of starch:
By combining the ground raw material with water, make a slurry. The source and the amount of starch in the raw material determine the water-to-raw-material ratio. The starch granules must be gelatinized by heating the slurry. This entails stirring while raising the mixture’s temperature to a predetermined level (often between 60 and 70°C). If necessary, modify the slurry’s pH. Alpha-amylase enzymes can be introduced to help break down starch into simpler sugars, to separate the starch slurry from the insoluble components, filter the mixture.
Separation and purification:
Now the starch slurry is left to settle so that it can separate from the other ingredients then cleanse the starch with water to remove any remaining contaminants after decanting the liquid portion. Further separating starch from water can be done using centrifugation or hydrocyclones.
Drying and milling:
Depending on the intended use, methods like drum drying, flash drying, or air drying to remove excess water from the starch are used to achieve the appropriate moisture content for storage and future use. The starch is next milled if it is determined to be necessary; this is typically done to achieve the desired size.
Quality control and storage:
Test the starch for parameters like moisture content, viscosity, gel strength, and purity to ensure it meets the required specifications, Store the prepared starch in moisture-proof containers to prevent degradation.
Modified starch suppliers: How to find these suppliers
Parameters to consider when choosing a supplier:
Choosing the best source of modified starch requires careful evaluation of several important aspects. These consist of product quality, cost, shelf life, industry experience, safety procedures, and effective delivery services. Setting these aspects as a top priority guarantees the acquisition of superior modified starch products that comply with manufacturing specifications.
Evaluating suppliers
To ensure a reliable and knowledgeable collaboration, it is essential to do in-depth investigation and assessment of prospective modified starch providers. Examining the supplier’s track record, reading through client testimonials, and confirming accreditations are essential for determining the supplier’s reliability in the market.
Product quality and safety:
An essential part of the decision-making process is evaluating the safety and quality of the modified starch products that a supplier provides. Authenticating certifications, comprehending the testing protocols of the supplier, and confirming compliance with industry standards are essential steps in securing the acquisition of high-quality and safe modified starch for food processing.
Delivery and customer service considerations:
Evaluation of the effectiveness of delivery services and the calibre of customer support offered by the supplier is crucial, in addition to product quality. Choosing a supplier who places a high value on punctual delivery, keeps lines of communication open, and provides outstanding customer service improves the procurement process as a whole and creates a long-lasting and fruitful collaboration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the starch manufacturer market is a dynamic ecosystem where factors such as delivery services, reputation, quality, and safety standards, along with adherence to testing procedures and industry standards, shape the landscape. With a diverse product range spanning from high-quality corn starch to specialized variants like tapioca and potato starch, manufacturers strive to offer exceptional starch products. The emphasis on affordability without compromising on quality underscores the importance of efficient manufacturing units and a robust supply chain. Buyers prioritize suppliers who ensure timely delivery, uphold safety in food products, and offer various types of modified starches, including oxidized, acetylated, hydrolyzed, and cross-linked starches. By evaluating these criteria, stakeholders can forge partnerships with suppliers that deliver both reliability and excellence.




